

The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite index developed by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) to measure a country’s average achievements in human development.
It was introduced in 1990 by economists Amartya Sen and Mahbub ul Haq to shift the development discourse beyond income.
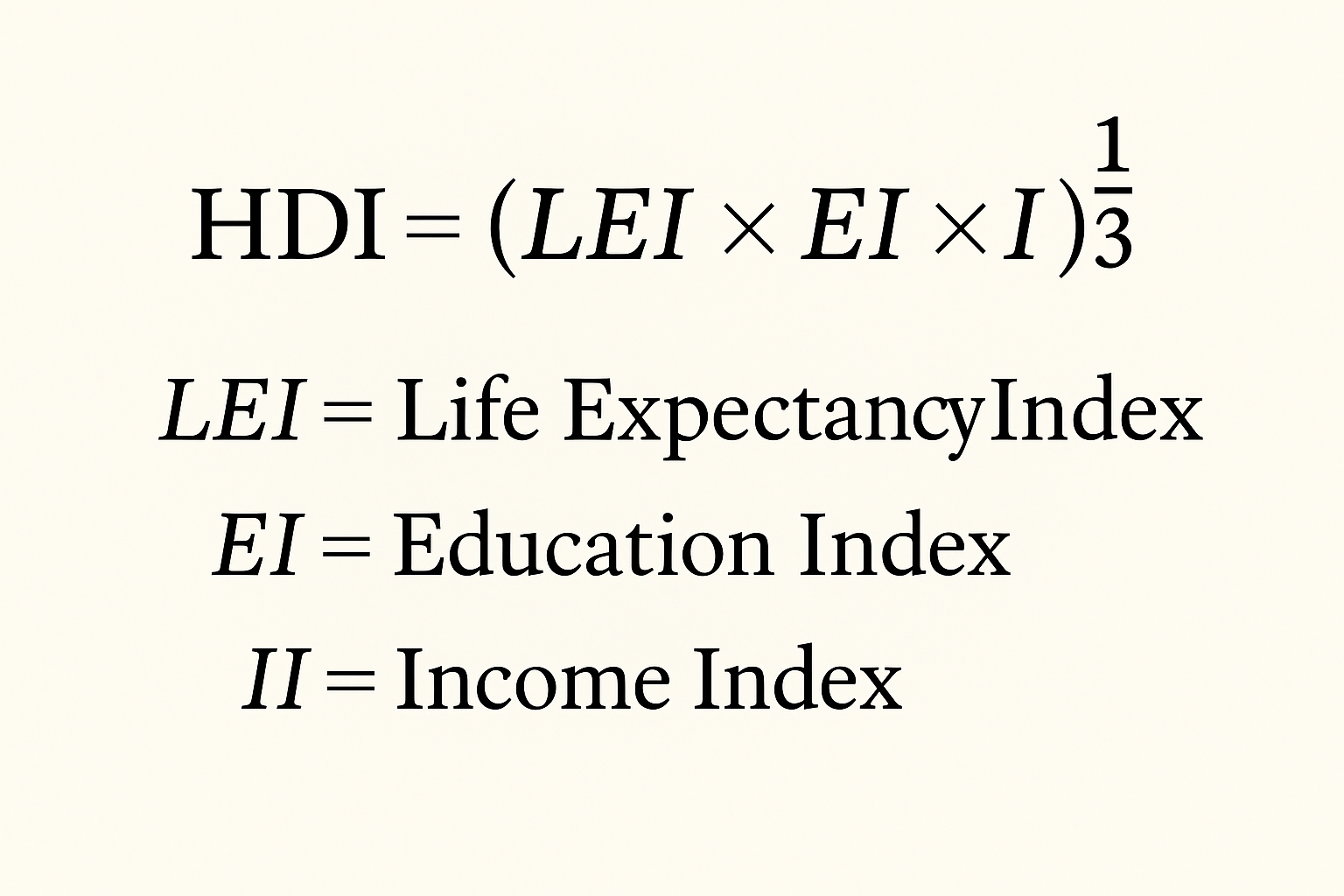
It shows average performance in three important areas of human development:
HDI = (LEI×EI×II)1/3
| HDI Value Range | Development Category |
|---|---|
| 0.800 – 1.000 | Very High Human Development |
| 0.700 – 0.799 | High Human Development |
| 0.550 – 0.699 | Medium Human Development |
| Below 0.550 | Low Human Development |
The three indicators of HDI are
UNDP releases the list of the rankings of the countries according to their HDI in order to seek the attention of the policymakers, the media, and the non-governmental organizations of the countries to change the approach from general economic statistics to human outcomes.
| Indicator | Value (2023 Data) |
|---|---|
| Life Expectancy | 72 years (highest ever for India) |
| Expected Years of Schooling | 13 years |
| Mean Years of Schooling | 9 years |
| Gross National Income (GNI) per capita | $9,046.76 (PPP 2021) |
| Index Name | What It Measures |
|---|---|
| IHDI (Inequality-adjusted HDI) | Penalizes HDI for inequality in distribution |
| GDI (Gender Development Index) | HDI gap between men and women |
| GII (Gender Inequality Index) | Reproductive health, empowerment, and labor |
| MPI (Multidimensional Poverty Index) | Deprivations across education, health, living std. |
| Country | HDI Rank (2023) | HDI Value (2023) |
|---|---|---|
| China | 75 | 0.788 |
| Sri Lanka | 78 | 0.776 |
| Bhutan | 127 | 0.665 |
| India | 130 | 0.685 |
| Bangladesh | 130 | 0.685 |
| Nepal | 145 | 0.622 |
| Pakistan | 168 | 0.544 |
| Rank | Country | HDI Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Iceland | 0.972 |
| 2 | Norway | 0.970 |
| 3 | Switzerland | 0.970 |
| ... | ||
| 130 | India | 0.685 |
| 193 | South Sudan | 0.388 |
Comments
Write Comment