WHAT IS A COOPERATIVE BANK?
A cooperative bank is a financial institution that is owned and controlled by a group of people who are also customers of the bank. These banks follow the cooperative principle of one person, one vote, and provide services such as savings and loans to both members and non-members. Cooperative banks were initially established to provide credit to members and liberate the underprivileged from the clutches of unscrupulous moneylenders who demanded exorbitant interest rates.
Cooperative banks established on a cooperative basis, primarily to provide credit and financial services to their members, especially in rural and semi-urban areas. They play a crucial role in inclusive banking, particularly for small farmers, traders, and low-income groups.
Types of Cooperative Banks in India
Cooperative banks are broadly categorized into two segments
Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs)
Operate in urban and semi-urban areas. Serve small borrowers, traders, and salaried employees. Can be scheduled or non-scheduled banks UCBs are regulated by both the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the State Registrar of Cooperative Societies.
Rural Cooperative Banks
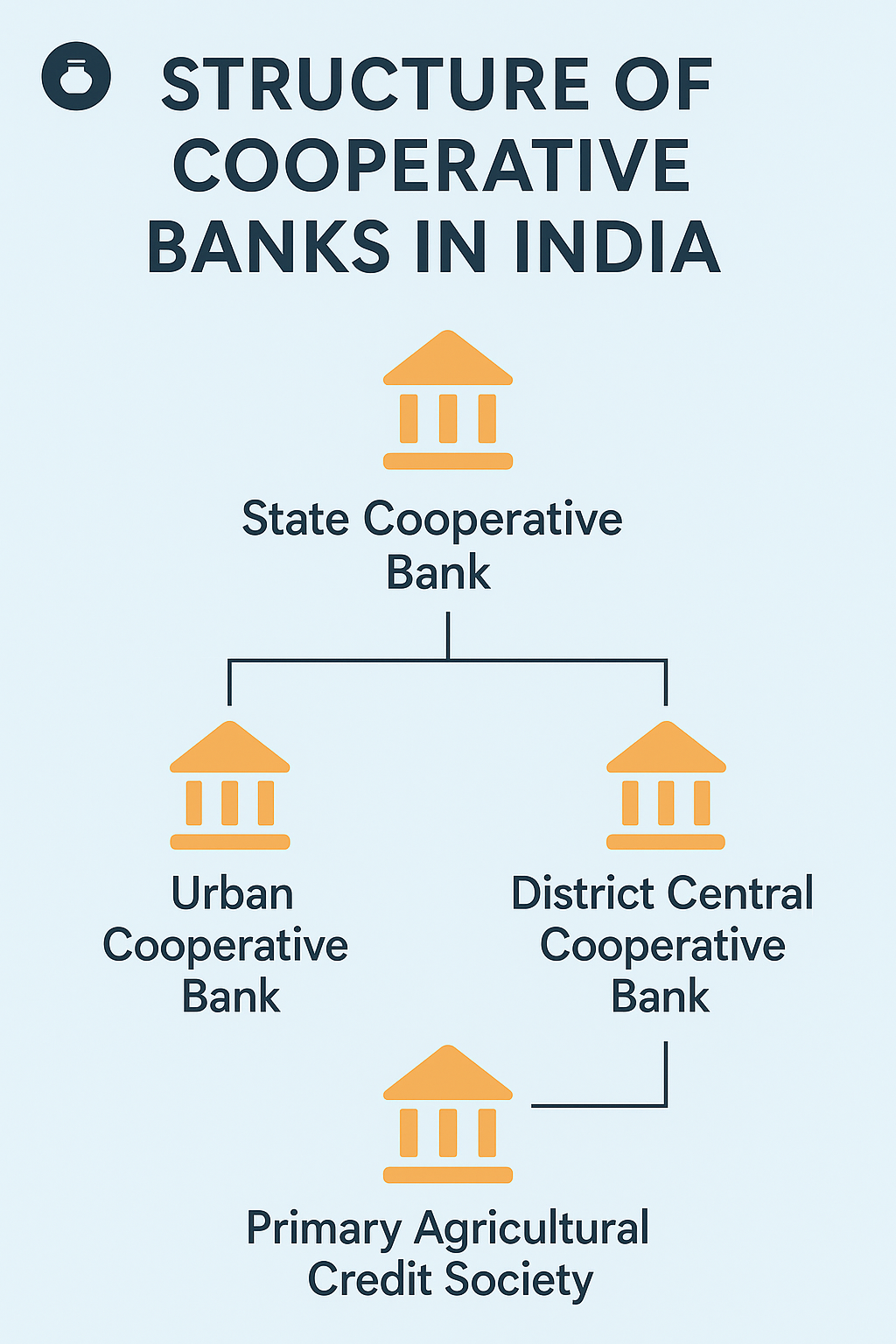
3 TIER STRUCTURE OF SHORT TERM COOPERATIVES : (from bottom to top)
- Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) : These are the basic building blocks of the cooperative banking structure. PACS operate at the grassroots level, typically at the village or small-town level. They directly interact with individual farmers and rural residents. The primary function of PACS is to provide credit and other financial services to their members.
- District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs): DCCBs operate at the district level and act as intermediaries between PACS and higher-level institutions. They provide financial assistance to PACS and coordinate their activities. CCBs function as the apex cooperative banks for PACS within a district. Usually they don’t give loans directly but in case in an area PACS is not functioning, DCCBs can also lend to the farmers.
- State Cooperative Banks (SCBs): SCBs operate at the state level and serve as apex institutions for CCBs. They provide financial assistance and guidance to DCCBs. SCBs are responsible for coordinating and overseeing the functioning of cooperative banks within the state.
PURPOSE?
Cooperative banks in India play a crucial role in the country's financial system by promoting financial inclusion and catering to the credit needs of various sectors, especially in rural and semi-urban areas. These banks operate on the cooperative principles of self-help and mutual assistance.

- Credit Functions: Cooperative banks provide credit facilities to farmers, agricultural workers, and rural entrepreneurs. They offer various types of loans, including crop loans, term loans, and working capital loans, to meet the diverse needs of the agricultural sector.
- Deposit Functions: Cooperative banks accept deposits from their members and the public. They offer savings accounts, fixed deposits, and recurring deposit schemes to encourage savings.
- Marketing and Processing Functions: Some cooperative banks engage in marketing and processing activities to help farmers sell their agricultural produce at fair prices. They may also provide processing facilities for certain agricultural products.
- Supply of Agricultural Inputs: Cooperative banks often supply agricultural inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides to their members at reasonable rates, contributing to the overall development of the agricultural sector.
- Financial Inclusion: Cooperative banks play a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion by reaching out to rural and underserved areas. They provide banking services to people who may not have access to traditional banking institutions.
- Developmental Functions: Cooperative banks participate in various developmental programs initiated by the government and NABARD. These programs aim to uplift the rural economy through infrastructure development, capacity building, and skill enhancement.
- Community Development: Cooperative banks often engage in community development activities, including education, healthcare, and other social welfare initiatives, contributing to the overall well-being of their members and the community.
WHO REGULATES THEM?
Cooperative banks are often regulated under both banking and cooperative legislation. Cooperative banks in India are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India through Banking regulation act 1949 and Banking laws (cooperative society) act 1955 and are registered under the States Cooperative Societies Act. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the primary regulatory authority overseeing the functioning of cooperative banks. NABARD also plays a regulatory role, particularly in matters related to agricultural and rural development.
CHALLENGES FACED
- Poor governance and political interference.
- High levels of non-performing assets (NPAs).
- Limited capital and professional management.
- Inadequate technology adoption.
- Weak internal controls and auditing standards.
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
- Banking Regulation (Amendment) Act, 2020 : Brought UCBs and multi-state cooperative banks under full supervision of RBI. Aimed to improve governance, transparency, and depositor protection.
- Consolidation & Digitalization: Efforts are being made to consolidate weak banks and promote digitization for better efficiency.
ROLE OF NABARD
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD): While NABARD is not a cooperative bank itself, NABARD plays a crucial role in supporting and regulating cooperative banks in India. NABARD acts as the apex institution at the national level for coordinating the activities of various institutions involved in rural development, including cooperative banks.




Comments
Write Comment